Sign up for our newsletter!
Your data will be handled in compliance with our privacy policy.
Your data will be handled in compliance with our privacy policy.
Research paper published in the proceedings at ICE 2021, the 3rd International Conference on Electrolysis June 20 – 23, 2022 Golden, Colorado USA.
M Bylund, R Andersson, A M Saleem, E Passalacqua, V Marknäs, V Desmaris • August 20, 2022
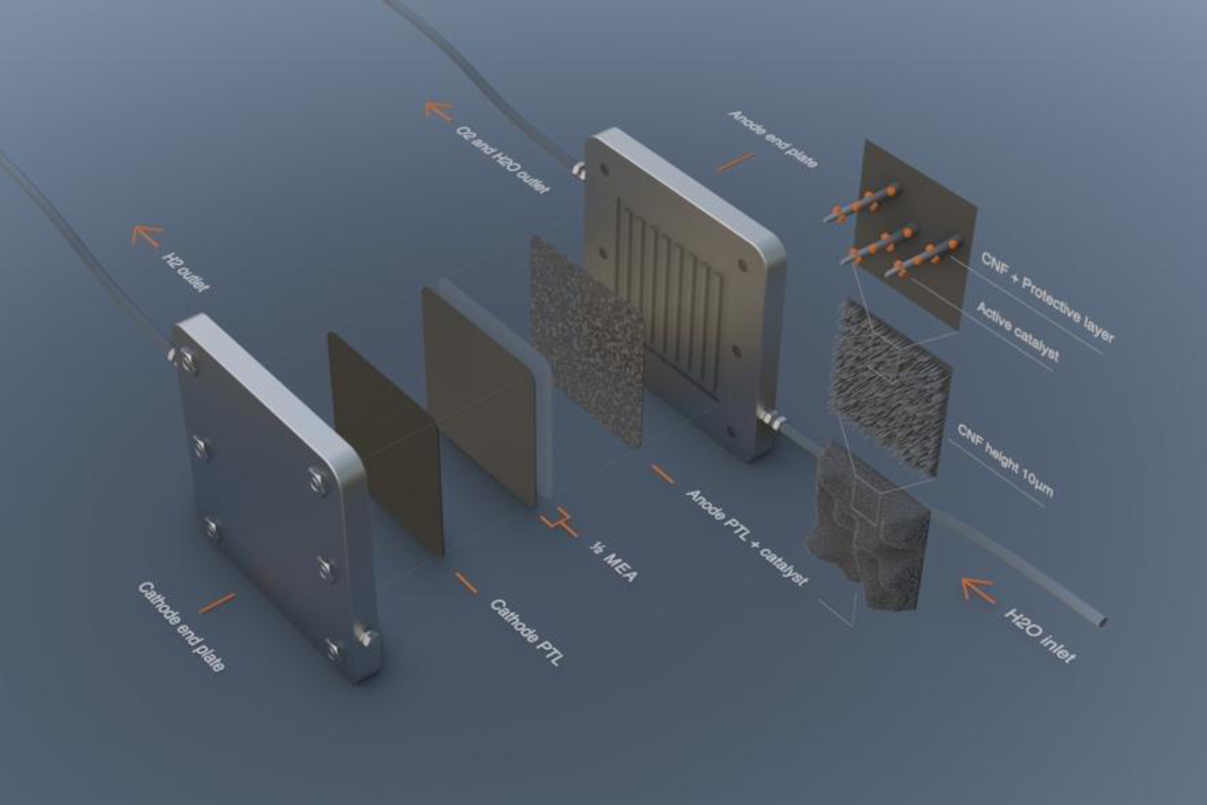
PEMWE is recognized as a key technology for sustainable hydrogen production. However, the necessity of using platinum group metals (PGMs) as catalysts sets up a barrier for establishing GW-scale systems. Especially on the anode side for oxygen evolution, the loading of iridium catalyst must be reduced significantly from currently 2 mgIr cm‑2 to 0.05 mgIr cm‑2 level to enable large scale application of PEMWE [1]. Even though substantial progress has been made, there remain tremendous challenges to make PEMWE work at ultra-low loadings in practice.
Vertically aligned carbon nanofibers (CNF) create low-tortuosity conducting 3D nanostructures over porous transport layers (PTLs), acting as supports for ultra-low loading of iridium catalyst with non-compromised performance. Proton exchange membrane water electrolysis (PEMWE) is envisaged to be more efficient using such advanced PTLs.
Read more on: https://learn.mines.edu/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/ICE2021_ProgramComplete01.with-links.6.17.22.pdf (page 24–25).
Your data will be handled in compliance with our privacy policy.